The overall effectiveness of carbon reduction in many countries has not met expectations, turning “climate change” into a “climate emergency”. Faced with the threat of extreme climate disasters, the earth is ushering in the 6th mass extinction, endangering the survival of human civilization, and also affecting the daily life of all people on the earth. Although the real estate brokerage industry is not a major producer of carbon emissions, Sinyi Realty still, implements climate governance in compliance with the TCFD structure of “governance, strategy, risk management, and metrics and targets”, revealing climate-related risk management to enhance climate resilience, promote sustainable business operations and integrate industry forces and all human power to resolve disasters caused by “climate emergency”.
Climate-related Risks and Opportunities in Compliance with TCFD
1. Governance
The Board of Directors (The Board)
Is the top-level monitoring unit of climate change management, being responsible for reviewing annual risk management report, execution report, and audit report to ensure the effectiveness of climate-related risk management system.
Total Ethical Management Committee (TEM Committee)
Is the highest ESG promotion unit in Sinyi Realty, which convened by Chairman and Directors, and the members senior management, including the General Manager, C-Suites, the Vice General Manager of staff, and the Vice General Manager of sales.
The TEM Committee is responsible for climate-related project management. The CFO reports to the Board on results of climate-related projects quarterly. The Board reviews ESG impacts, performance and strategic goals regularly; complies with the risk management procedures to reduce the threats caused by occasional climate events.
Corporate Ethics Sustainability Committee
Is convened by Chief Ethics Officer and consisted of management level of different departments or business units in Sinyi Group. In the monthly meeting climate-related or ESG-related topics such as sustainable branches or energy convention projects are discussed and synergy is created because of resource integration.
ESG Working Groups
Are lead by the managers of responsible departments respectively to implement the sustainable or climate-related projects approved by the Corporate Ethics Sustainability Committee, the TEM committee and the Board. Meetings are held on demand by each working group.

2. Strategy
- Define time horizons: short-term: 1 year(~2023), medium-term: 1~10 years(~2030), long-term: 10~30 years(~2050)
- Analyze the financial and non-financial impacts of climate-related risks and climate-related opportunities; explore business opportunities, strategies and action plans.
- Apply two climate-related scenario analysis of “NZE+NDCs and SSP5-8.5” to analyze physical risks and transition risks.
- NZE+NDCs:
Referred to the IEA net-zero emission scenario(NZE), the 1.5°C goal of Paris Agreement, and Taiwan 2050 Net Zero Pathway(NDCs), the transitional risks and opportunities of moving towards a low-carbon economy and decarbonized energy were taken into consideration. - SSP5-8.5:
Referred to IPCC AR6 SSP5-8.5 scenario and its estimated situation in Taiwan by Taiwan Climate Change Projection Information and Adaptation Knowledge Platform (TCCIP), the physical risks of increased number of strong typhoons/ rainfall volume and intensity/ average temperature were taken into consideration.
- NZE+NDCs:
3. Risk Management
- The Board of Directors, the top-level monitoring unit of risks management, is responsible for reviewing the annual risk management report and audit report to ensure the effective implementation of the climate-related risk management system.
- In response to possible climate-related physical risks and transition risks, we reassess the climate-related impact every year, explore business opportunities, strategies and action plans in a systematic way.
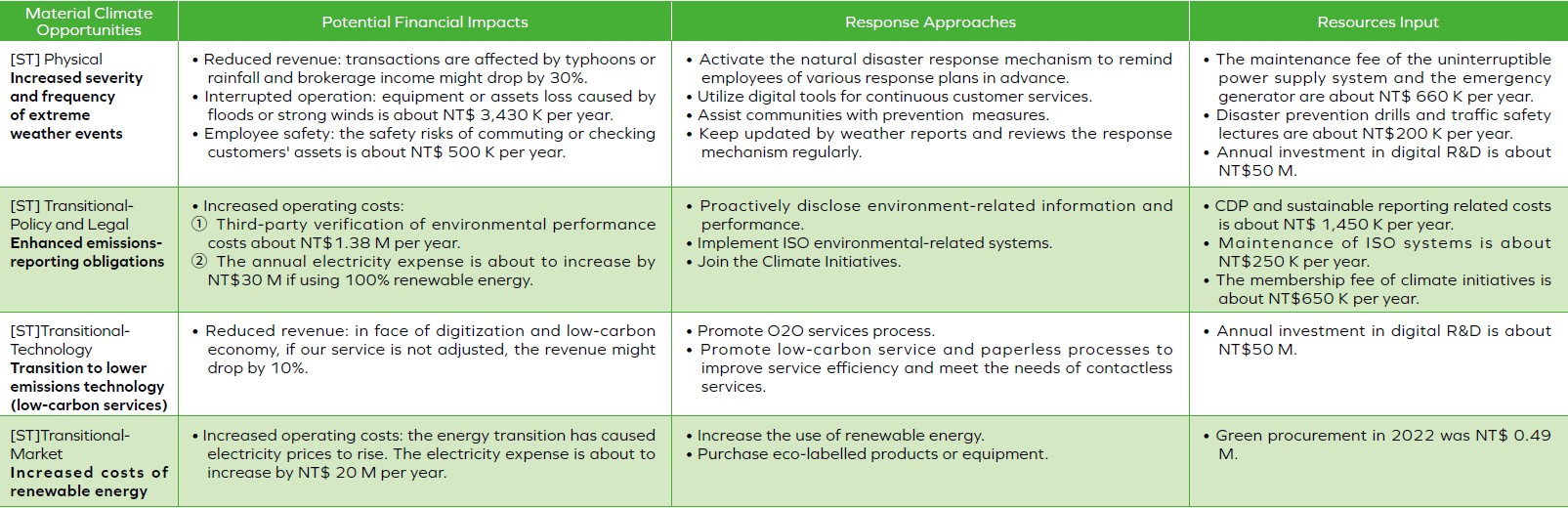
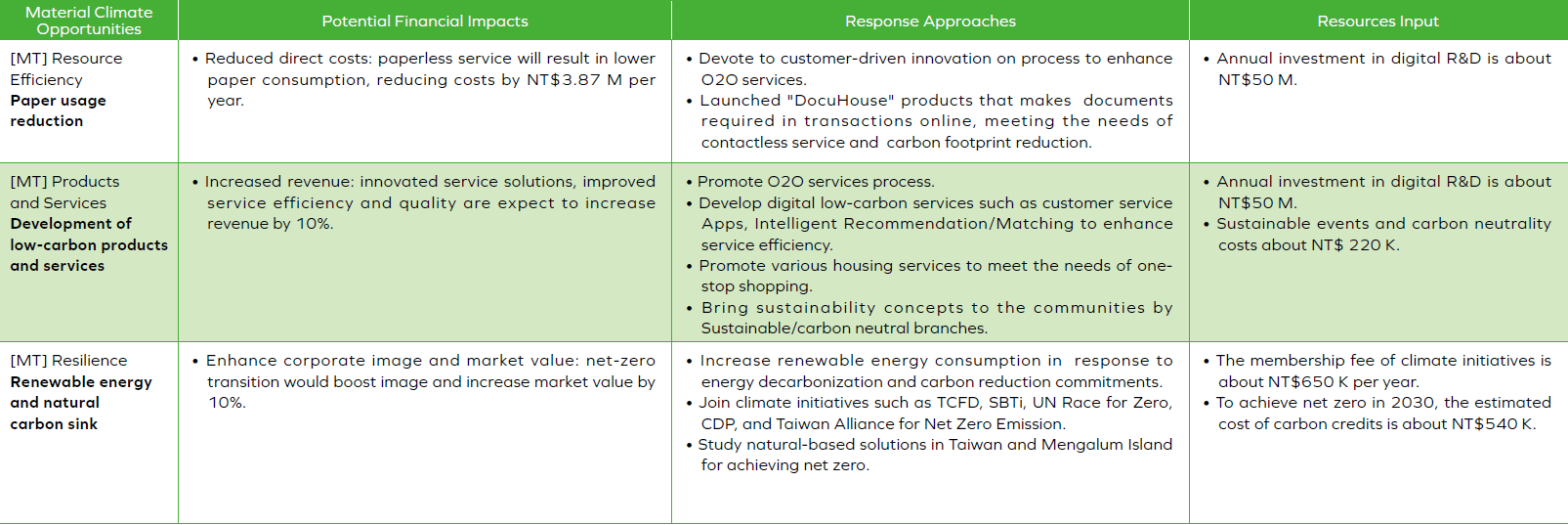
- The risk evaluation is based on the severity and probability. The identified primary climate-related risk drivers are “transition to lower emission technology”, “enhanced emissions-reporting obligations”, “increasing energy costs”, and “Increased severity of extreme weather events such as cyclones and floods”. The identified primary climate-related opportunity drivers are “reduce paper usage”, “development and/or expansion of low emission goods and services”, “participation in renewable energy programs and adoption of energy efficiency measures”, and “Renewable energy and natural carbon sink.
Climate-related Risk Matrix
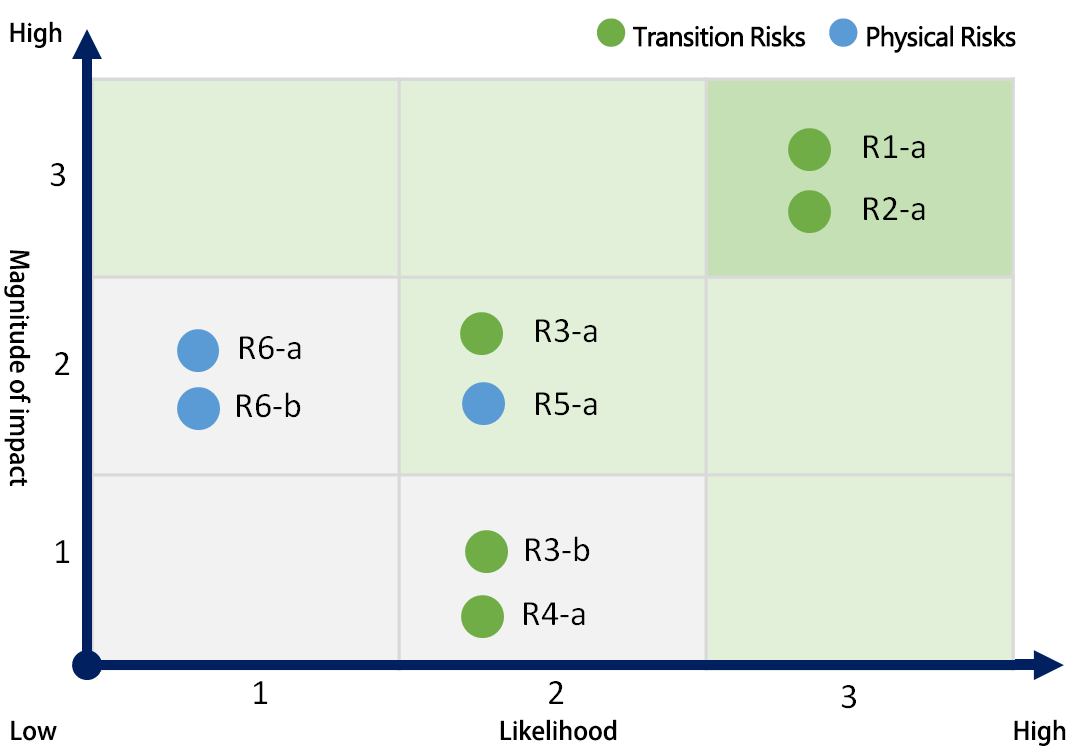
| No. | Risk type | Primary climate-related risk driver |
|---|---|---|
| R1-a | Policy and Legal | Enhanced emissions-reporting obligations |
| R2-a | Technology | Transitioning to lower emission technology |
| R3-a | Market | Increase energy cost |
| R3-b | Market | Changing customer behavior |
| R4-a | Reputation | Increased stakeholder concern or negative stakeholder feedback |
| R5-a | Acute | Increased severity of extreme weather events such as cyclones and floods |
| R6-a | Chronic | Changes in precipitation patterns and extreme variability in weather patterns |
| R6-b | Chronic | Rising mean temperatures |
*primary climate-related risk drivers are marked in bold.
Climate-related risk materiality ranking: We identified primary climate-related risk driver as ” Transitioning to lower emission technology,” “Enhanced emissions-reporting obligations,” “Increase energy cost” and “Increased severity of extreme weather events.”
Climate-related Opportunities Matrix
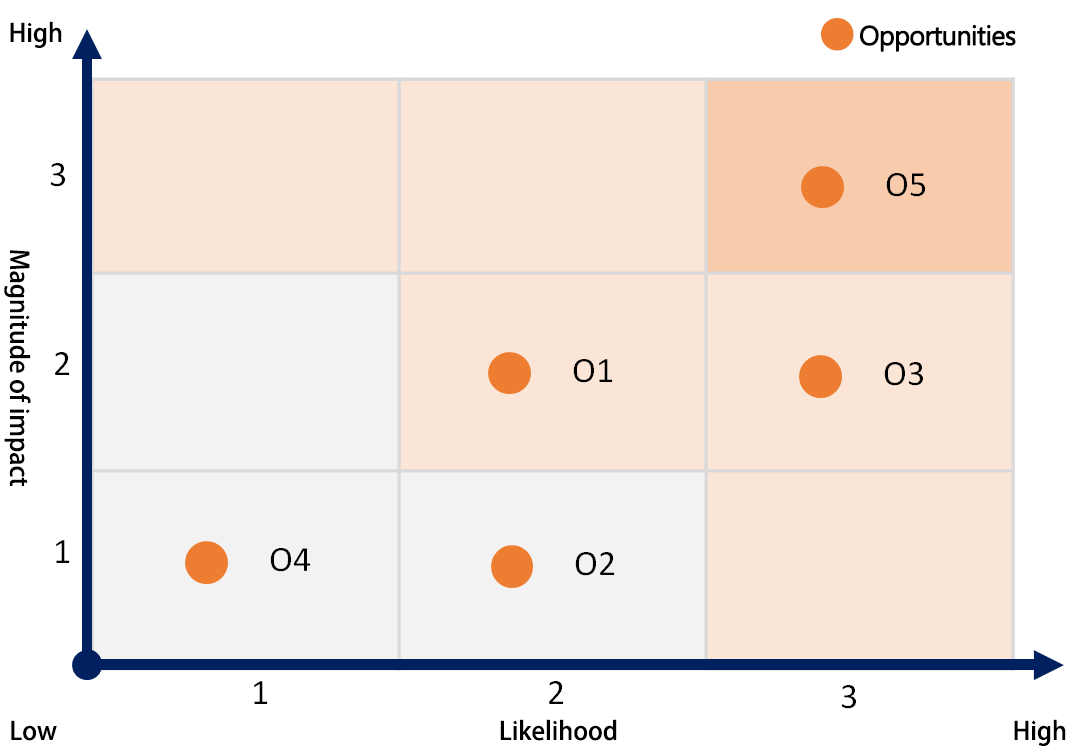
| No. | Opportunity type | Primary climate-related opportunity driver |
|---|---|---|
| O1 | Resource Efficiency | Reduce paper usage |
| O2 | Energy Source | Use of lower-emission sources of energy |
| O3 | Products and Services | Development and/or expansion of low emission goods and services |
| O4 | Markets | Use of public-sector incentives |
| O5 | Resilience | Renewable energy and natural carbon sink |
*primary climate-related risk drivers are marked in bold.
Climate-related opportunity materiality ranking: We identified primary climate-related opportunity driver as ”Reduce paper usage,” ”Development and/or expansion of low emission goods and services “ and “Renewable energy and natural carbon sink.”
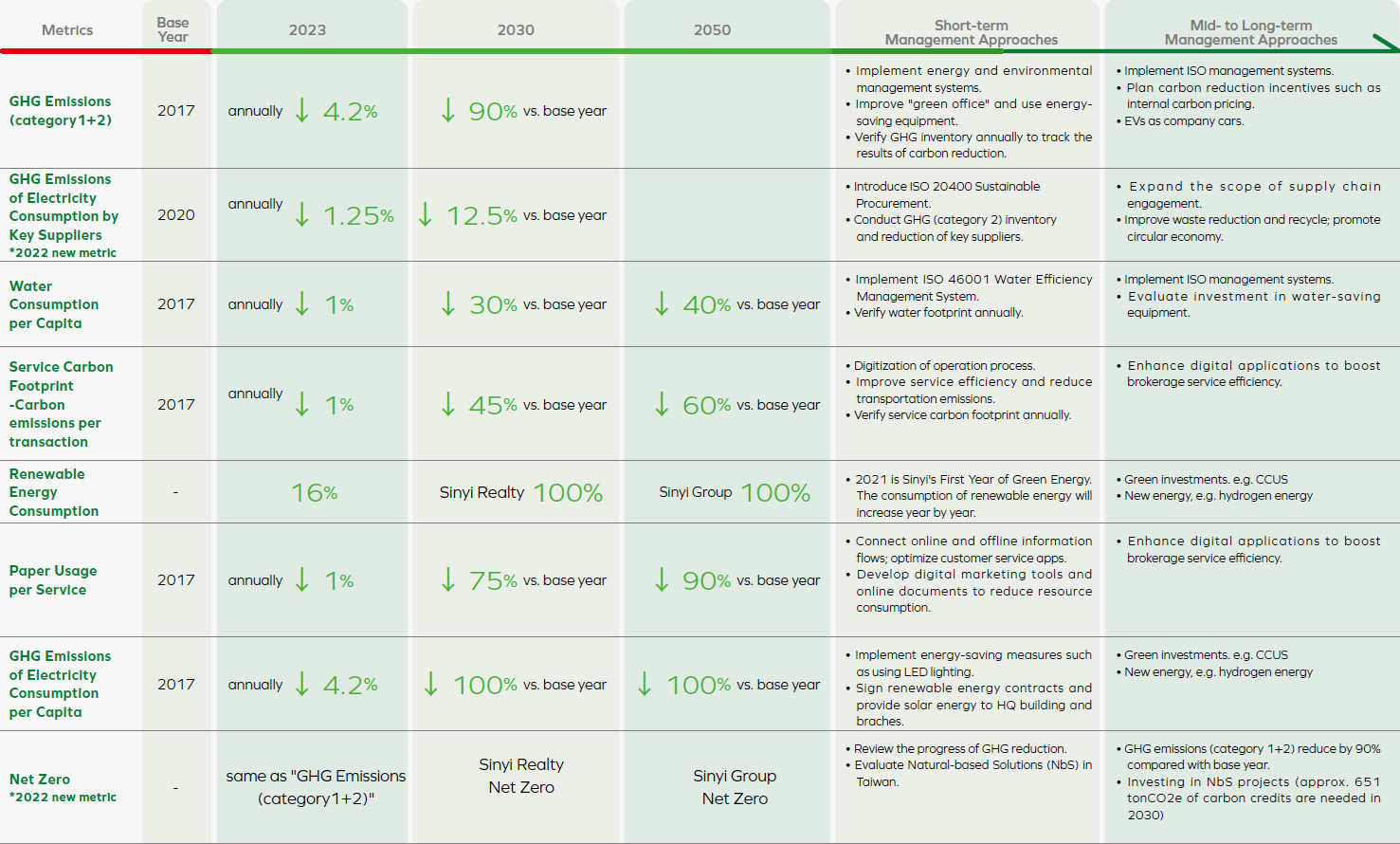
4. Metrics and Targets
Sinyi Realty develops green management strategies and goals, launches shrot, mid and long-term management approaches, reviews the progress, and discloses environmental performance.
5. Net Zero Transition Plan
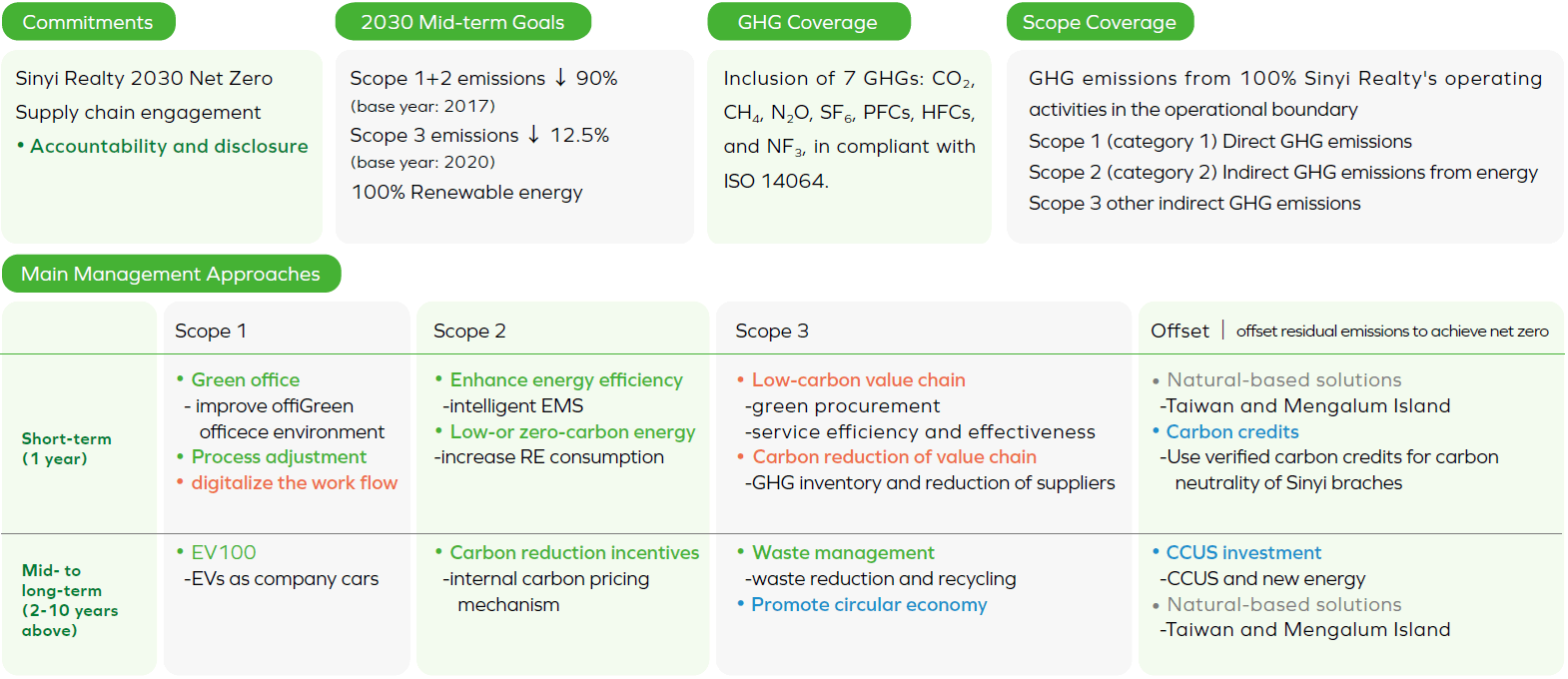
In response to the opportunities arising from climate emergency, Sinyi Realty has established strategies and goals that are in line with the principle of “Get to Net Zero”, and expects to influence its value chain to move towards a low-carbon economy.
 TCFD Conformity Statement
Sinyi Realty TCFD Report
TCFD Conformity Statement
Sinyi Realty TCFD Report